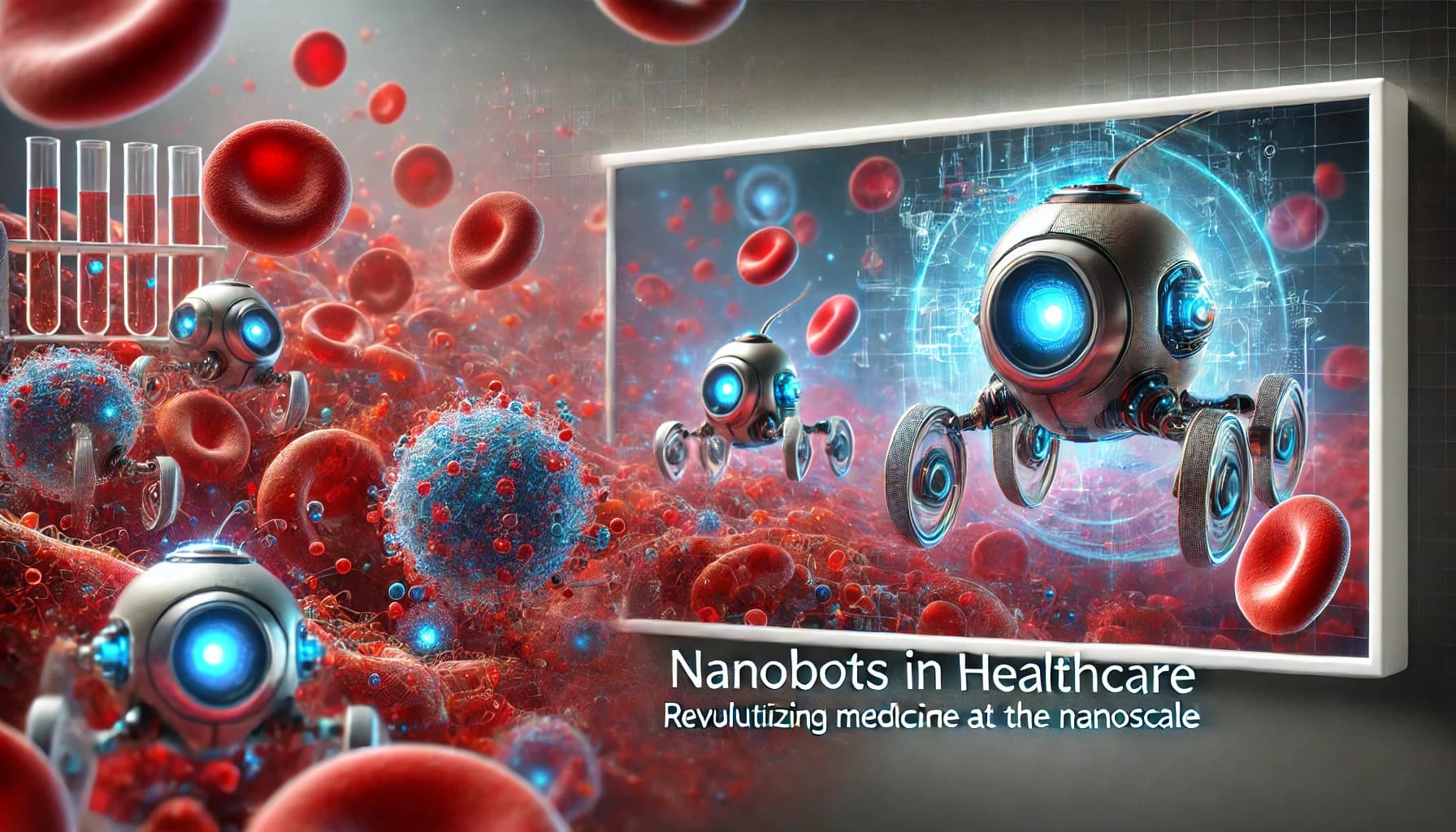
Nanobots in Healthcare: Revolutionizing Medicine at the Nanoscale
FREEIntroduction
Advancements in nanotechnology are paving the way for groundbreaking innovations in healthcare. Among these, nanobots—microscopic robots operating at the nanoscale—are poised to transform medical diagnostics and treatments. This article explores the role of nanobots in healthcare, their applications, benefits, and the challenges they present.
What Are Nanobots?
Nanobots, or nanorobots, are devices ranging from 1 to 100 nanometers in size, significantly smaller than a human blood cell. These tiny machines can navigate through the human body to perform precise medical tasks, such as diagnosing diseases, delivering drugs, and repairing tissues.
Applications of Nanobots in Healthcare
Targeted Drug Delivery: Nanobots can transport medications directly to diseased cells, enhancing treatment efficacy and minimizing side effects. This precision is particularly beneficial in cancer therapy, where targeted delivery can reduce damage to healthy tissues.
Disease Diagnosis and Monitoring: Equipped with sensors, nanobots can detect molecular changes indicative of diseases, enabling early diagnosis and continuous health monitoring.
Surgical Procedures: Nanobots offer the potential for minimally invasive surgeries by navigating through the bloodstream to perform tasks like clearing arterial blockages or repairing tissues.
Cancer Treatment: Researchers are developing nanobots capable of identifying and destroying cancer cells, offering a targeted approach to cancer therapy.
Benefits of Nanobots in Medicine
Precision: Nanobots operate at the cellular level, allowing for highly accurate interventions.
Minimally Invasive: Their small size enables procedures that are less invasive than traditional surgeries, reducing recovery times.
Real-Time Monitoring: Nanobots can continuously monitor health parameters, providing real-time data for proactive healthcare management.
Challenges and Considerations
While the potential of nanobots is immense, several challenges must be addressed:
Biocompatibility: Ensuring that nanobots do not trigger adverse immune responses is crucial.
Manufacturing Complexity: Producing nanobots at scale with consistent quality remains a significant hurdle.
Ethical and Regulatory Issues: The deployment of nanobots raises ethical questions and requires robust regulatory frameworks to ensure safety and efficacy.
Future Prospects
The field of nanobots in healthcare is rapidly evolving. Ongoing research aims to overcome current challenges, with the goal of integrating nanobots into mainstream medical practice. As technology advances, we can anticipate more sophisticated nanobots capable of performing complex medical tasks, potentially revolutionizing the way we diagnose and treat diseases.
Conclusion
Nanobots represent a frontier in medical technology, offering the promise of more precise, efficient, and less invasive healthcare solutions. While challenges remain, the ongoing research and development in this field hold the potential to significantly improve patient outcomes and transform the landscape of modern medicine.
References: